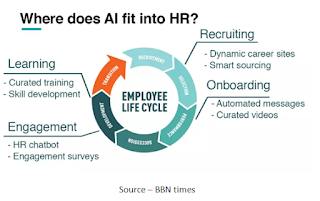
Introduction
Employee well-being and occupational health and safety (OHS) are two interconnected areas that are essential for ensuring the health, safety, and productivity of employees. Employee well-being is a broad concept that encompasses physical, emotional, and social well-being. OHS is concerned with identifying and mitigating workplace hazards and preventing work-related injuries and illnesses.
Together, these two areas form a critical partnership that can help organizations promote a healthy and safe workplace culture, boost employee morale and retention, and improve business outcomes.
Interconnection between employee well-being and OHS ((Armstrong Handbook
of HRM, 2014)
One of the key ways in which employee well-being and OHS are connected is through the impact of work-related stress on health and safety outcomes. Employees who experience high levels of stress are more likely to engage in unsafe work behaviors and experience workplace accidents and injuries .Thus, addressing work-related stress is critical for promoting both employee well-being and OHS.
Another area of intersection between employee well-being and OHS is in the realm of ergonomics. Ergonomics is concerned with the design of work spaces and equipment to maximize safety, comfort, and productivity. By designing work spaces and equipment that support good ergonomics, organizations can reduce the risk of musculoskeletal disorders and other physical injuries.
Types of employee well-being (Alexandra
Marinak)
- Financial well-being – being able to meet the personal financial needs successfully
- Career well-being – being able to work and meet their career objectives
- Emotional well-being – being able to manage stress or emotional struggles
- Physical well-being – being able for basic functioning and accomplishing tasks
- Community well-being – having a connection with others and feeling a sense of belonging in the workplace
- Leisure well-being – being able to spend on creative, interesting and entertaining pursuits in their life
Reasons why employee well-being and OHS are concerns (Armstrong Handbook
of HRM, 2014)
- Employers have a duty to adopt a socially responsible approach to looking after their people.
- Employers do so because this will increase the commitment of the employees towards the organization and will help to establish it as a ‘best place to work’.
- Employers are responsible for creating a good work environment as a part of the total reward system.
- Improved well-being also contributes for goal achievement, risk taking and finding practical solutions for challenges that arise.
- Improved well-being also contributes to decreased absenteeism and increased retention and engagement.
- A proper OSH workplace would give reduced health care expenses
Strategies that can be used for employee well-being and OHS.
Establish comprehensive workplace wellness programs that focus on promoting healthy lifestyle behaviors and addressing work-related stress. These programs can include initiatives such as stress management training, physical activity programs, and healthy eating campaigns.
Conduct regular OHS audits and risk assessments to identify and address workplace hazards, and provide workers with training and resources to promote safe work practices.
Role of HR leaders to promote employee well-being and OHS
- Balance work with play – organize mood-boosting, community-building and social gatherings through which employees could refresh and reconnect
- Cultivate gratitude – create an open culture for appreciation and reward which would infuse a positive vibe into the work community
- Encourage mindfulness – set the foundation (by some breathing exercises or meditation) for smart decision making and high quality work.
Factors that would lead to negative employee well-being and OHS
- Leadership style – a poor management style would create a higher stress level
- Workload – heavy workload due to improper staffing and resource allocation
- Lack of social support – comparison of performance between peers would make the employees not support each other
- Personal commitment – personal issues outside the organization (pregnancy, relationship conflict, death of loved ones)
- Improper ergonomics – work spaces and equipment that do not facilitate smooth work flow
Measuring employee well-being
HR team can conduct surveys on topics such as compensation, engagement, belonging, workload, and career goals.
HR can maintain a work-force data that would highlight high rate of absenteeism or low productivity
HR can have in-person check-ins with employees and identify issues if any
Conclusion
Employee well-being and OHS are two critical areas that are interconnected and essential for promoting a healthy, safe, and productive workplace. By recognizing the importance of this partnership and implementing strategies to promote both areas, organizations can create a culture of safety and well-being that benefits workers and the business as a whole.
References
Alexandra Marinak. (no date) Employee well-being. Resources for employees (online)
Available at https://resources.workable.com/stories-and-insights/employee-wellbeing-caring-for-your-people
Accessed on
06th April 2023
Bob. (no date) What is employee well-being? bob (Online)
Available at https://www.hibob.com/hr-glossary/employee-wellbeing/
Accessed on
06th April 2023
Joseph
Htel. (no date) Armstrong’s Essential Human Resource Management Practice -
Michael Armstrong & Stephen Taylor.
Academia (Online)
Available at
https://www.academia.edu/19545696
Accessed on
04th April 2023